The early detection of malignant tumors has always been a major medical problem. Although the high survival rate of malignant tumors in the early stage, patients who develop into the middle and late stages are often difficult to cure. Therefore it is very significant for early detection of malignant tumors. There are no obvious symptoms in early stage and the tumor are easily treated as simple diseases. Traditional medical detection methods often have problems such as complicated operation process, complicated preparation and long time-consuming detection, and the cost of tumor detection is relatively expensive, so it is easy to miss the optimal treatment time. Therefore, a fast, convenient, and low in loss detection technology is urgently needed to solve the problem of early detection of malignant tumors to meet medical needs. At present, laser induced breakdown spectroscopy has wide research value and application prospects in the field of biomedicine due to its unique advantages such as rapid and simple sample preparation.
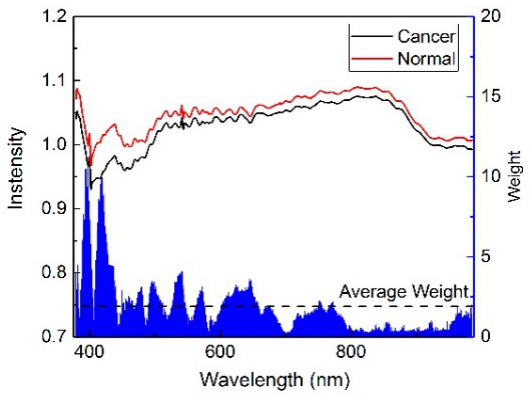
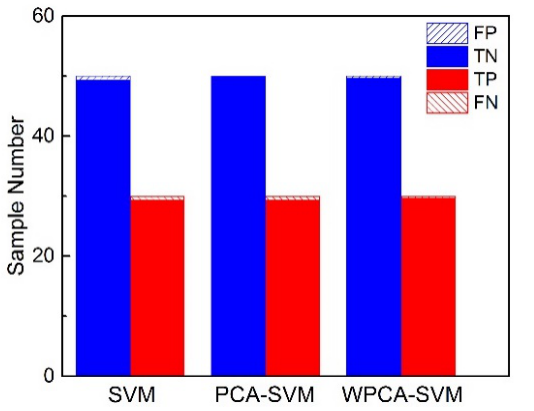
Associate Professor Guo Lianbo, whoes is from the LIBS Research Group of the Laser Advanced Manufacturing Technology Research Group of Wuhan National Optoelectronics Research Center, reached an in-depth cooperation with Dr. Honglin Jin from Tongji Medical College to detect the difference in serum from malignant tumors and normal controls from the perspective of spectroscopy. Doctoral student Y.W. Chu, F. Chen and T. Chen in the group performed hyperspectral (HSI) detection on nasopharyngeal carcinoma serum. Due to the small spectral difference, to improve the detection accuracy and reduce the hardware cost of detection, the weight-adjusted principal component analysis method and support vector machine (WPCA-SVM) are combined for pattern recognition. The results showed that the recognition accuracy, sensitivity and specificity of the prediction set increased from 98.49%, 97.91% and 98.83% to 99.15%, 98.79% and 99.36%, respectively. The spectral range of the simultaneous detection decreased from 606.06 nm to 394.46 nm. WPCA-SVM effectively improves the accuracy of diagnostics while also reducing hardware costs. This effectively promotes the research and application of hyperspectral detection in the diagnosis of malignant tumors.
This work has been published in Optics Express (Y.W. Chu, F. Chen, Y. Tang, T. Chen, YX. Yu, HL. Jin, L.B. Guo, Y.F. Lu, and X.Y. Zeng, "Diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma from serum samples using hyperspectral imaging combined with a chemometric method," Opt. Express 26, 28661-28671 (2018)).
The research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51429501, 61575073 and 81503026).
(a)
Fig (a) The weight distribution
(b)
Fig(b) The result of diagnosis