In recent years, interest-driven, unscrupulous manufacturers have been adding cheaper meat species into expensive ones, for example, adding pork to beef, or selling “zombies meat”, etc. Adulteration of meat products seriously endangers people's healthy life, which causes adverse effects to food safety in China. However, the disadvantages of traditional methods, such as complex operation and time required restrict their application. Therefore, a fast and in situ detection technology is urgently needed to solve the problem of fast detection of meat products. At present, laser induced breakdown spectroscopy has a wide range of research value and application prospects in the industry of meat products and food safety because of its unique advantages, such as rapid in situ and simple sample preparation.
The research group of Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics Guo Lianbo, an associate professor, led a doctoral student Y.W.Chu, and two postdoctoral fellows, S.S.Tang and Z.Q.Hao introduced LIBS detection of meat products identification. Multiplicative scatter correction (MSC) was adopted to first pretreat the spectrum for correction of spectrum scatter. Then the corrected spectra were identified by using the K-nearest neighbor (KNN) model. The results showed that the identification rate improved from 94.17% to 100% and the prediction coefficient of variance (CV) decreased from 5.16% to 0.56%. This means that the accuracy and stability of meat species identification using MSC and LIBS simultaneously improved. the proposed method can be a valuable tool for meat species identification using LIBS.
This work has been published in Optics Express (Y.W. Chu, S.S. Tang, S.X. Ma, Y. Y. Ma, Z.Q. Hao, Y.M. Guo, L.B. Guo, Y.F. Lu, and X.Y. Zeng, "Accuracy and stability improvement for meat species identification using multiplicative scatter correction and laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy," Opt. Express 26, 10119-10127 (2018) ).
The research was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51429501 and 61575073) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No.2017M622415).
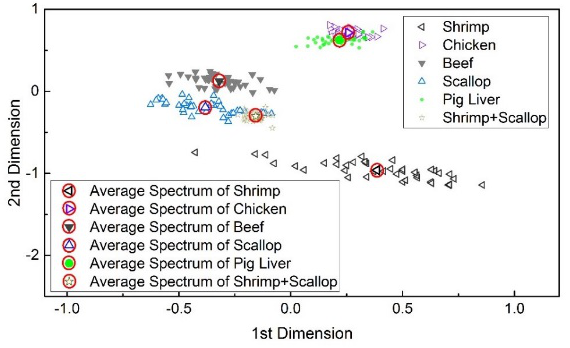
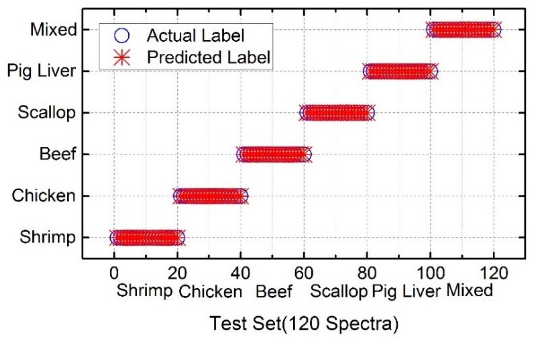
(a) (b)
Fig (b) The relative position of each spectrum (c)the result after MSC