Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy has the advantages of fast, real-time online, no sample pretreatment, and simultaneous multi-element detection in elemental detection and analysis. It has obtained preliminary applications in the fields of industry, agriculture, environmental science, and medicine. At present, the quantitative analysis of laser probes usually adopts multi-standard calibration method. Although the detection accuracy of this method is high, a series of standard samples are needed to establish a calibration curve. However, in the field of space exploration, environmental protection, geological survey and other lack of standards, the application of multi-standard methods have great limitations. On the other hand, there is no need for a free calibration method for the standard, and since there is no standard as a reference, the detection accuracy is low. Therefore, in order to balance the accuracy and simplicity of quantitative analysis, exploring a single-sample or less-sample calibration method has become one of the current research priorities.
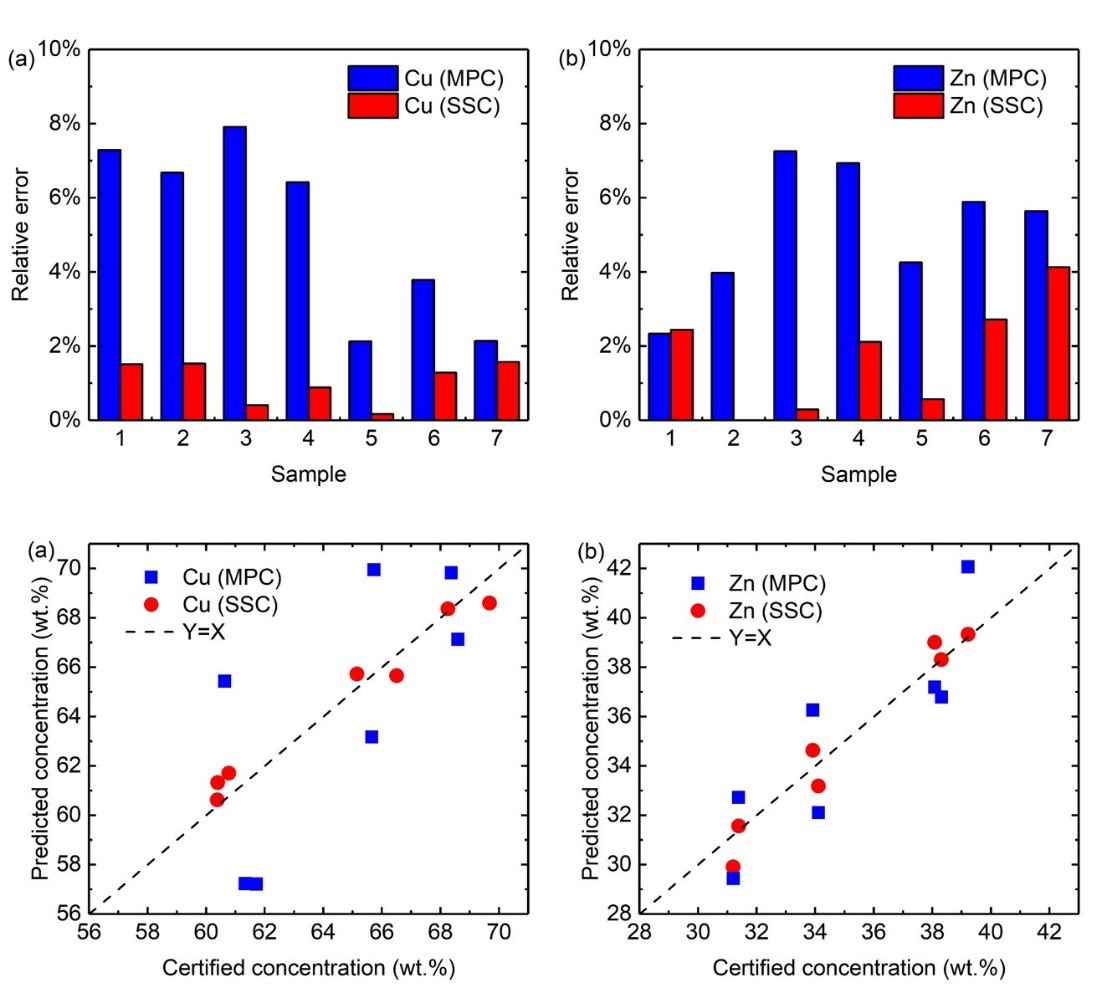
Figure. Comparison of quantitative analysis using SSC-LIBS and MPC-LIBS in Brass samples: (a) Cu and (b) Zn.
Assoc. Prof. Guo Lianbo and Master Yuan Rui of advanced laser manufacturing group (WNLO) proposed a new method for quantitative analysis in Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using single-sample calibration (SSC-LIBS). The calculation formula of this method is derived by the Lomkin-Scherbe formula. The elemental content of the sample to be tested can be obtained by simply using the full spectrum of a standard sample and the sample to be tested and substituting the spectral intensity of each element into the formula. In this study, SSC-LIBS was applied to the quantitative analysis of standard samples of brass alloy, microalloyed steel, and nickel-based alloy. Taking the brass sample as an example, the R2, RMSECV, ARE, and ARSD of the Cu element were improved from 0.40, 3.55 wt.%, 5.19%, and 16.22% to 0.97, 0.76 wt%, 1.05% and 1.15%, respectively, compared with the multi-sample calibration method. The results show that SSC-LIBS can significantly improve the accuracy and stability of quantitative analysis of major elements. SSC-LIBS provides a more convenient and accurate calibration method for the quantitative analysis of laser probes, which is of great significance for the application of laser probe technology in real life.
On March 7, 2019, the paper "Accuracy improvement of quantitative analysis for major elements in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy using single-sample calibration" was published in the Analytica Chimica Acta which belongs to the Elsevier (Analytica Chimica Acta, 2019, 1064: 11-16). This research was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61575073). The manuscript link:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.02.056.